Stacks
These are the data structures which have property that last item pushed in will be the first item to go out. So these are Last In First Out (LIFO) or First In Last Out (FILO) structures. This structure also sometime called as pushdown stack.
Two operations performed are Push and Pop.
The common practice is that we use a stack that grows in a direction of decreasing memory.
Consider an element is placed at a location assumed as Bottom of the stack, and when elements are pushed on to the stack, they placed in successively lower address locations.
A processor register is used to keep track of the address of the element of the stack that is at the top at any given time. This register is called as Stack Pointer.
It Could be one of the general purpose register or a register dedicated to this function.
Push operation can be implemented as
Subtract #4,SP
Move NEWITEM, (SP)
Here the subtract instruction subtracts 4 from the contents of SP register and then places the content of NEWITEM on to the stack. The SP is decremented by 4 before the Move operation.
Pop operation can be implemented as
Move (SP), ITEM
Add #4,SP
Here the contents pointed by SP register is placed in ITEM and then contents of the SP register is added with the value 4 .
If Auto decrement and Auto increment instructions are used then they can be used to perform Push and Pop operation
Push:
Move Newitem,-(SP)
Pop:
Move (SP)+,ITEM
Consider Bottom of the stack as 2000 and the top of the stack as 1500
So we can not Pop beyond 2000 and we can not Push beyond 1500
Safe pop
compare #2000,SP
Branch>0 to Empty Error
Move (SP)+,ITEM
Safe push
compare #1500,SP
Branch<=0 to Full Error
Move NEWITEM,-(SP)
Note: Compare Instruction destination-source and sets the conditional flags
SUBROUTINES
- In a given program, it is often necessary to perform a particular subtask many times on different data values. Such a subtask is usually called a subroutine.
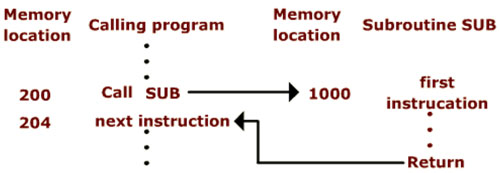
- When a program branches to a subroutine it is called calling the subroutine. The instruction that performs this branch operation is named a Call instruction.
- After a subroutine has been executed, the calling program must resume execution, continuing immediately after the instruction that called the subroutine.
- The subroutine is said to return to the program that called it by executing a Return instruction.
- The way in which a computer makes it possible to call and return from subroutines is referred to as its subroutine linkage method.
- The simplest subroutine linkage method is to save the return address in a specific location, which may be a register dedicated to this function. Such a register is called the link register.
- The Call instruction is just a special branch instruction that performs the following operations:
-Store the contents of the PC in the link register
-Branch to the target address specified by the instruction - The Return instruction is a special branch instruction that performs the operation:
-Branch to the address contained in the link register.
Figure illustrates the procedure of calling a subroutine and return
Lesson on Addressing Modes << Previous
Support us generously: contact@lessons2all.com
Our aim is to provide information to the knowledge seekers.





.jpg)



