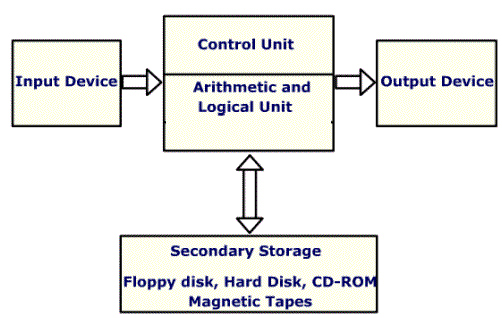
Lessons on Functional Units of Computers
- Input unit
- Output unit
- Memory
- Arithmetic and logic unit
- Control unit
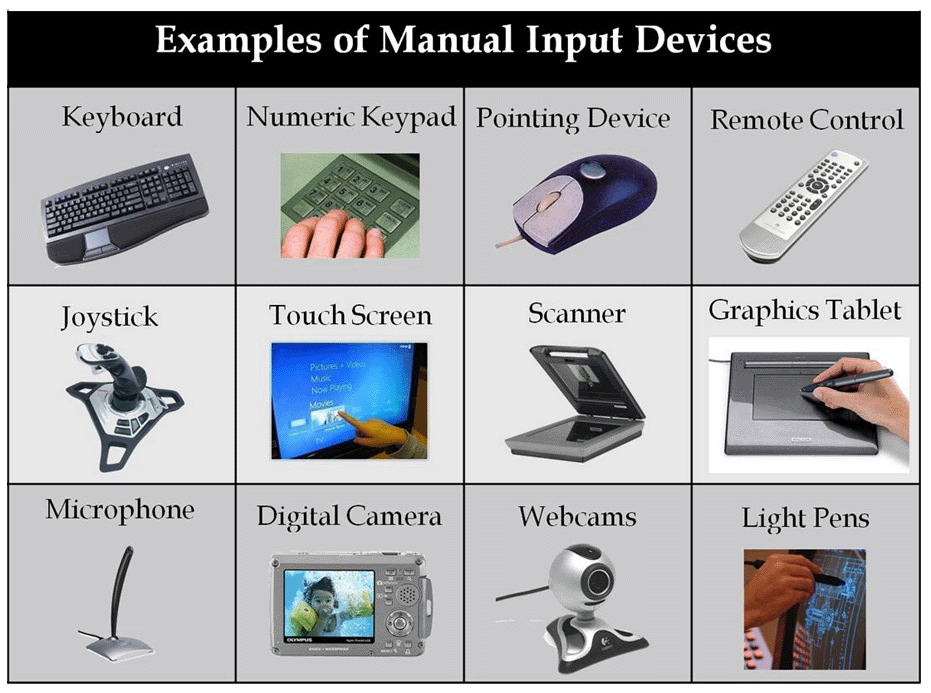
Input units
Input units are used to feed the data to the computers.
Different Input Units:
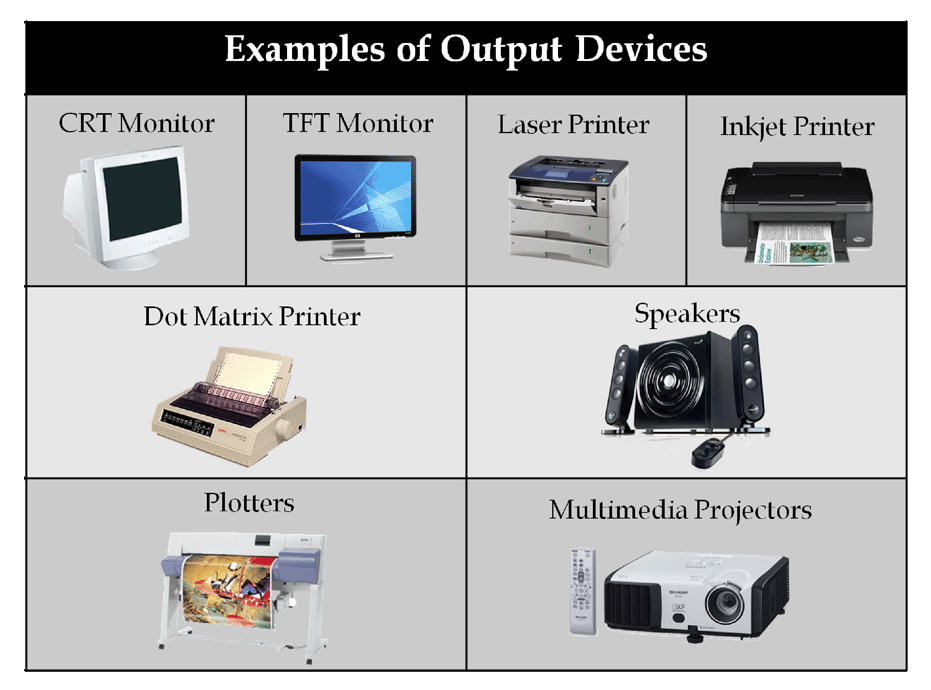
Output Units
Output units are used to give the results of processing to the user.
Different Output Units
Memory unit
Memory units are used to process and store the data/result
Computer memory system can be broadly classified into four groups:
Internal memory : These are the set of CPU registers
What are CPU registers?
- These registers are made up of group of flip flops
- Each flip flop will store one bit of memory
- Stores temporary results during the computation process.
- Cost of these registers is high.
Main Memory is made up of Random Access Memory (RAM) and Read Only Memory (ROM)
Features of Primary memory: Random Access Memory (RAM)
- RAM is volatile
- Made up of semiconductor storage cells.
- Each cell is capable of storing one bit of information. So word is group of these cells
- Processor can directly access the main memory
- During execution, program must be present in main memory
- Addresses are the numbers used to identify successive locations.
- Using these addresses contents from the memory is retrieved or written
Features of Main Memory: Read Only Memory (ROM)
- ROM is not volaitle, you can read the contents already written into it and can not write anything in it
- It contains the instructions which are used during the start up of computers
- The set of instructions present in ROM are called as Basic Input-Output System (BIOS)
Cache Memory
Features of Cache Memory
- Like RAM, Cache memory is also volatile
- Made up of semiconductor storage cells.
- Each cell is capable of storing one bit of information. So word is group of these cells
- Processor can directly access this memory
- It contains most frequently used instructions
- Addresses are the numbers used to identify successive locations.
- Using these addresses contents from Cache memory is retrieved or written
- Storage capacity of Cache is samll compared to RAM but it is more faster than RAM

Secondary Memory

Lessons on Basic structure of Computer << Previous
Next>> Lesson on Cache Memory and Memory Access modes
Support us generously: contact@lessons2all.com
Our aim is to provide information to the knowledge seekers.




.jpg)



